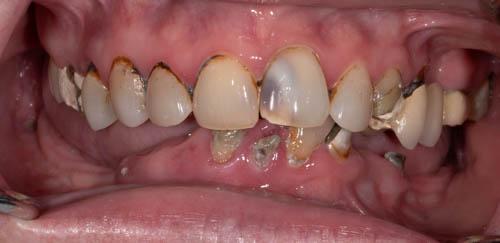
Xerostomia is the sensation of having a dry mouth, which can result from diminished saliva production.
Saliva is of utmost importance in the mouth for several reasons.
- Plays a critical role in the digestion process. As we chew our food, saliva assists in breaking food, facilitating its absorption in the digestive tract.
- Acts as a lubricant, aiding in speech and swallowing of food. It also helps soften the food, making it easier to manage within the mouth.
- Neutralizes acids produced by bacteria, thus protecting our teeth from decay.
- Washes away food debris, reducing the risk of dental plaque and gum disease.
- It contributes to the taste sensation, as it carries tastants to the taste buds, allowing us to enjoy and savor the flavors of our meals.
- Antimicrobial properties make it an essential component of our innate immune system. It contains various antimicrobial substances that help combat harmful bacteria, viruses, and fungi in the mouth.
- Maintains the equilibrium of beneficial bacteria while suppressing the growth of harmful ones.
Effects of Xerostomia on Teeth
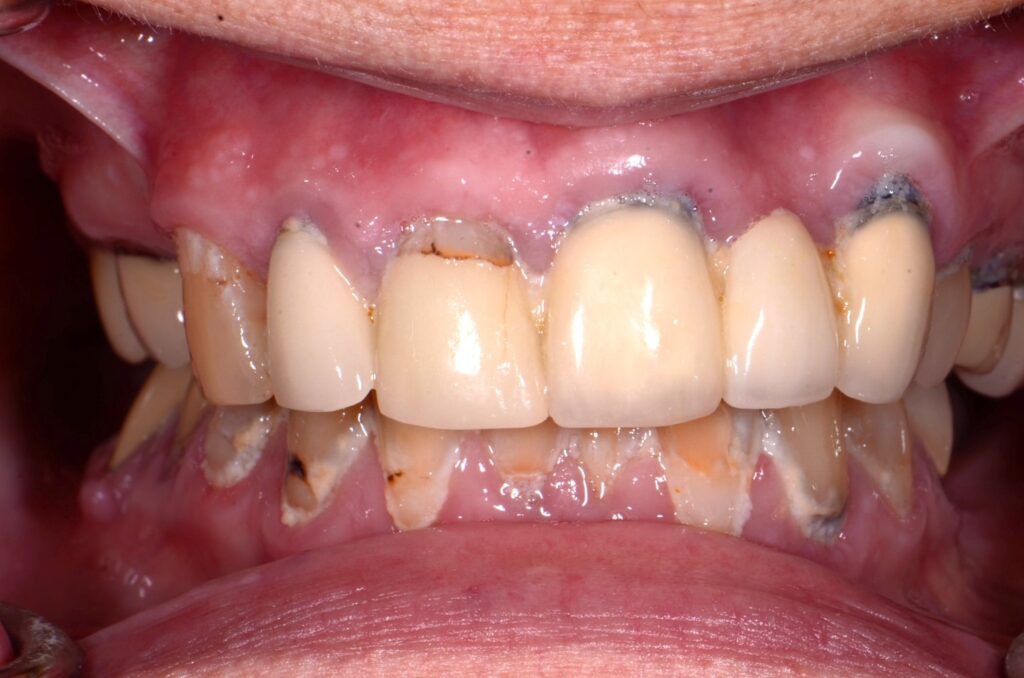
Causes of Xerostomia
Medication-Induced Dry Mouth: This category specifically relates to dry mouth caused by certain medications. Many prescription and over-the-counter drugs, such as antihistamines, antidepressants, and diuretics, can reduce salivary flow and cause dry mouth as a side effect.
Disease-Related Dry Mouth: Some medical conditions and diseases can directly or indirectly affect salivary flow and lead to dry mouth. Examples include Sjögren’s syndrome, diabetes, autoimmune disorders, HIV/AIDS, Parkinson’s disease, and others.
Radiation-Induced Dry Mouth: Patients undergoing radiation therapy for head and neck cancers may experience damage to the salivary glands, leading to reduced saliva production and dry mouth.
Neurological Dry Mouth: Dry mouth can occur due to nerve damage or neurological conditions that affect the nerves controlling the salivary glands.
Stress-Induced Dry Mouth: Emotional stress and anxiety can affect the autonomic nervous system and lead to dry mouth symptoms.
Sleep-Related Dry Mouth: Conditions such as snoring or obstructive sleep apnea can cause mouth breathing during sleep and contribute to dry mouth.
Unknown Cause (Idiopathic Dry Mouth): In some cases, dry mouth may not have a specific identifiable cause and is classified as idiopathic.
Effects of Xerostomia on Teeth